We are pleased to announce the release of ChEMBL 30. This version of the database, prepared on 22/02/2022 contains:
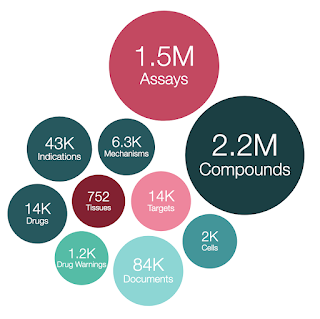
- 2,786,911 compound records
- 2,157,379 compounds (of which 2,136,187 have mol files)
- 19,286,751 activities
- 1,458,215 assays
- 14,855 targets
- 84,092 documents
Data can be downloaded from the ChEMBL FTP site: https://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/chembl/ChEMBLdb/releases/chembl_30/
Please see ChEMBL_30 release notes for full details of all changes in this release: https://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/chembl/ChEMBLdb/releases/chembl_30/chembl_30_release_notes.txt
New Deposited Datasets
EUbOPEN Chemogenomic Library (src_id = 55, ChEMBL Document ID CHEMBL4689842):
The
EUbOPEN consortium is an Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) funded
project to enable and unlock biology in the open. The aims of the
project are to assemble an open access chemogenomic library comprising
about 5,000 well annotated compounds covering roughly 1,000 different
proteins, to synthesize at least 100 high-quality, open-access chemical
probes and to develop infrastructure, technologies and platforms.
Screening data generated during this 5 year project will be deposited in
ChEMBL.
Donated Chemical Probes - SGC Frankfurt (src_id = 54, ChEMBL Document IDs CHEMBL4800721-CHEMBL4800732):
Data for new chemical probes has been added.
New Data Sources
Salvensis and LSHTM Schistosomiasis screening data (src_id=56):
IMI-CARE SARS-CoV-2 Data (src_id=57):
IMI-CARE SARS-CoV-2 Data (src_id=57):
Updated Data Sources
Scientific LiteratureOrange Book
Clinical Candidates
Gates Library compound collection
Patent Bioactivity Data
USP Dictionary of USAN and International Drug Names
Prodrug active ingredients
SARS-CoV-2 Screening Data
Manually Added Drugs
Donated Chemical Probes - SGC Frankfurt
Clinical Candidates
Gates Library compound collection
Patent Bioactivity Data
USP Dictionary of USAN and International Drug Names
Prodrug active ingredients
SARS-CoV-2 Screening Data
Manually Added Drugs
Donated Chemical Probes - SGC Frankfurt
Withdrawn Drugs
EUbOPEN Chemogenomic Library
MMV Pathogen Box
EUbOPEN Chemogenomic Library
MMV Pathogen Box
Patent Bioactivity Data include 10557 new activities from 29 patents from 2019 and 2020, as part of the
Illuminating the Druggable Genome (IDG) project. These have enabled 8
targets to be promoted to the Tchem classification (see
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7818358/).
Database Changes
No schema changes.Funding acknowledgements:
Work
contributing to ChEMBL30 was funded by the Wellcome Trust, EMBL Member
States, Open Targets, National Institutes of Health (NIH), EU Innovative
Medicines Initiative 2 (IMI2) and EU Horizon 2020 programmes. Please
see https://chembl.gitbook.io/chembl-interface-documentation/acknowledgments for more details.
If you require further information about ChEMBL, please contact us: chembl-help@ebi.ac.uk
# To receive updates when new versions of ChEMBL are available, please sign up to our mailing list: http://listserver.ebi.ac.uk/mailman/listinfo/chembl-announce
# For general queries/feedback or to report any problems with data, please email: chembl-help@ebi.ac.uk
Comments